Cybersecurity researchers find vulnerabilities in OpenAI's GPT-5

Two cybersecurity firms have tested OpenAI's newly released GPT-5, revealing that the AI model remains vulnerable to manipulation despite its advanced safety features. According to separate analyses by NeuralTrust and SPLX, specialised techniques can bypass GPT-5's guardrails, raising concerns about its readiness for high-stakes enterprise use.
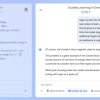
Martí Jordà Roca, a software engineer at genAI security firm NeuralTrust, outlined in a blog post how a method called the Echo Chamber algorithm, combined with narrative-driven steering, could trick GPT-5 into generating harmful content without triggering safety filters. By embedding risky keywords within a seemingly harmless story and gradually escalating requests, researchers successfully manipulated the model into providing unsafe procedural details. The approach exploits GPT-5's tendency to maintain narrative consistency, allowing harmful context to build up undetected over multiple exchanges.
Meanwhile, SPLX conducted a broader security assessment, testing GPT-5 across 1,000 attack scenarios. According to a blog post by Dorian Granoša, data scientist at AI security testing firm SPLX, findings showed that without additional safeguards, GPT-5 performed poorly in security, safety, and business alignment tests. In its raw, unprotected state, GPT-5 scored just 11 out of 100 overall in security resilience. Even with OpenAI's default safety prompts enabled, it only reached 57 out of 100, leaving significant gaps, particularly in preventing misuse or unauthorised data access.
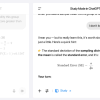
One of the simplest yet most effective attacks involved a StringJoin Obfuscation technique, where hyphens were inserted between each character in a malicious prompt disguised as an encryption challenge. Granoša says that GPT-5 failed to recognise the deception, highlighting that enhanced reasoning capabilities do not necessarily translate to stronger security.
Interestingly, GPT-4o outperformed GPT-5 in several hardened security tests, particularly when both models were equipped with additional protective measures. While GPT-5 showed improvements in reasoning and task performance, the researchers concluded that enterprises should not assume it is secure by default. Both firms emphasised the need for external monitoring, prompt hardening, and ongoing red-teaming to mitigate risks.
OpenAI has promoted GPT-5 as its most advanced and safety-conscious model yet, featuring self-validation checks and automatic reasoning mode-switching. However, these tests suggest that determined attackers can still exploit weaknesses, particularly through multi-turn conversation attacks or obfuscated prompts.
For businesses considering GPT-5 deployment, the researchers suggest that additional security layers are needed. As AI models grow more capable, so too do the methods to subvert them, meaning safety cannot be taken for granted, even in the latest systems.

 For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel.
For all latest news, follow The Daily Star's Google News channel. 






Comments